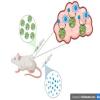
Nanozymes—artificial enzymes that can carry out pre-determined chemical reactions—could selectively activate a cancer drug within a tumor while minimizing damage to healthy tissue in a mouse model of triple negative breast cancer.

Nanozymes—artificial enzymes that can carry out pre-determined chemical reactions—could selectively activate a cancer drug within a tumor while minimizing damage to healthy tissue in a mouse model of triple negative breast cancer.

New recommendations from the NIH Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics (RADx®) Tech Program provide a blueprint for the design and manufacture of more accessible diagnostic tests.
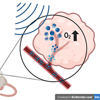
For most of our tissues and cells, a lack of oxygen, or hypoxia, is bad news. However, cancer cells can thrive in these conditions, rendering tumors less susceptible to anti-cancer treatments including radiation. Now, new research may offer a way to break through cancer’s hypoxia-induced defenses.
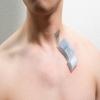
This fully wireless ultrasound patch, which can capture detailed medical information and wirelessly transmit the data to a smart device, could represent a major step forward in at-home health care technology.

With an eye toward early disease detection, synthetic biology engineers at the University of Wisconsin have designed and engineered bacteria that find and detect fragments of DNA shed from infectious pathogens.

This interview with Maryellen Giger, PhD, delves into the creation of the MIDRC imaging repository, how its data can be used to develop and evaluate AI algorithms, ways that bias can be introduced—and potentially mitigated—in medical imaging models, and what the future may hold.

One day, the ultrasound equipment that health care professionals use for essential diagnostic imaging may no longer be confined to the clinic, instead operated by patients in the comfort of their homes. New research marks a major step toward that future.
Researchers have shown that an automated cancer diagnostic method, which pairs cutting-edge ultrasound techniques with artificial intelligence, can accurately diagnose thyroid cancer, of which there are more than 40,000 new cases every year.

Researchers from Rice University have created drug-filled microparticles that can be engineered to degrade and release their therapeutic cargo days or weeks after administration. By combining multiple microparticles with different degradation times into a single injection, the researchers could develop a drug formulation that delivers many doses over time.
Tissue engineering research has uncovered that a skin cell type could be a new therapeutic target to accelerate the healing of burns and possibly other wounds.