
The Scanning Probe Microscopy Unit of the BEPS Shared Resource specializes in the following:
- Sub-nm resolution imaging of molecular complexes, supported lipid bilayers, cells, and tissues
- Molecular recognition, protein unfolding
- Force spectroscopy, visco-elastic properties
- Simultaneous, co-localized AFM and fluorescence (including TIRF and confocal) microscopy
- Mathematical modeling, finite element analysis
We are located in Building 13 on the NIH campus.
Atomic Force Imaging and Spectroscopy
AFM:
- Sub-nm resolution imaging of macromolecular complexes (including protein-protein, protein-DNA, and/or RNA), supported lipid bilayers, cells and tissues under ambient conditions
- Force spectroscopy: nano-indentation strategies to map viscoelastic, adhesion and other properties at nm resolution (including single molecules, lipid bilayers, live cells and tissues)
- Studies of protein unfolding
Molecular Recognition: Antigen recognition by binding events with antibody-functionalized probes. Immuno-AFM: Molecular recognition of protein-antibody complexes by direct AFM imaging. Co-localized immuno-fluorescence and immuno-AFM.
Mathematical Modeling: Mathematical modeling of biophysical systems, image analysis methodologies, finite element analysis.
Auditory Mechanics:
Project examples
Nucleus mechanical properties of HMGN5 over-expressing cells (Dr. M. Bustin, CCR, NCI)
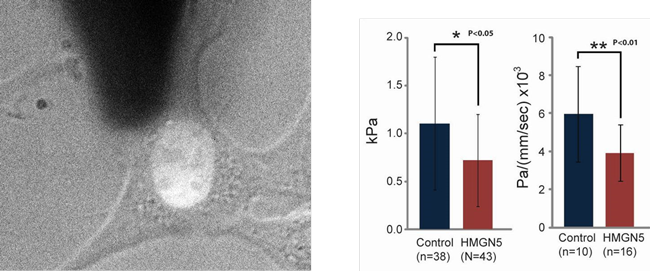
Cell visco-elastic properties were measured on live cells with the AFM
Novel DNA-RNA complexes (Dr. S. Adhya, CCR, NCI)
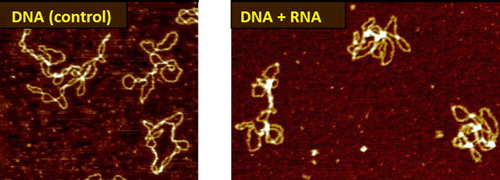
Novel bacterial RNA binds and bridges DNA double-strands

