NIBIB-funded research drives progress in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of middle ear infections.

NIBIB-funded research drives progress in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of middle ear infections.
Bioengineers have developed biocompatible self-assembling “piezoelectric wafers,” which can be made rapidly and inexpensively to enable broad use of implantable muscle-powered electromechanical therapies.
NIH-funded researchers at Carnegie Mellon University have demonstrated the potential of a neuromodulation approach that uses low-intensity ultrasound energy, called transcranial focused ultrasound—or tFUS.

Nanofiber-based treatments stimulate the body to mount its own biological attack on immune disorders.

A change of instructions in a computer program directs the computer to execute a different command. Similarly, synthetic biologists are learning the rules for how to direct the activities of human cells.
This study investigates how the nucleocapsid protein, or N protein, of the SARS-CoV-2 virus packages the viral genome.
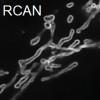
A team of NIH microscopists and computer scientists used a type of artificial intelligence called a neural network to obtain clearer pictures of cells at work even with extremely low, cell-friendly light levels.

NIBIB-funded researchers are investigating long-lasting, customizable nanobubbles for ultrasound contrast agents.

The new technique is capable of printing the models 10-50 times faster than the industry standard—in minutes instead of hours— a major step in the quest to create 3D-printed replacement organs.

One-year into implementation of the NIH RADx initiative, the IEEE Open Journal of Engineering in Medicine and Biology has dedicated a specialissue to exploring the innovative structure and operation of the RADx Tech program.